Anatomy Of Kidney
- These are a pair of bean shaped organs present just in-front of the posterior abdominal wall on both sides of vertebral coloumn.
- They extend from T12 to L3 vertebrae.
- The right kidney is present at a slightly lower level than in the left kidney.
- They are placed slightly orbitly upper core is close to the vertebral column. Lower core is away from the vertebral column.
 |
| Image 01 : Anatomy of Kidney. |
Covering Of Kidney :
- Each Kidney has upper pole which is related to the supra renal gland and a lower pole.
- It has got two borders ; Later border is convex; Medial border shows a notch called as hilum.
- The hilum will give passage to renal artery, renal vein and ureter.
- The kidney has two surface, arterior surface is convex. It is related to the other abdominal organs.
- Posterior surface is flat.
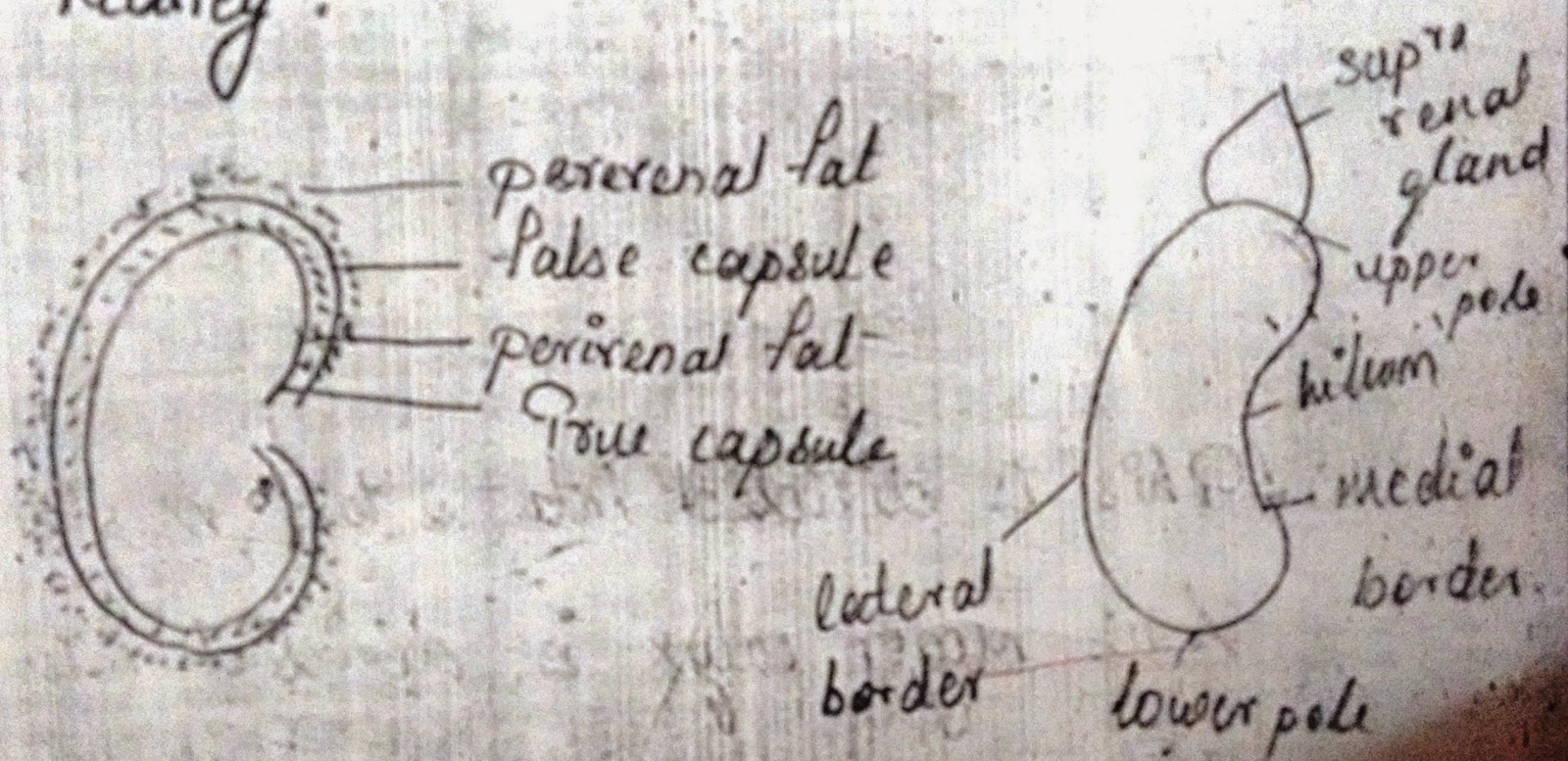 |
| Image 02 : Layers of Kidney. |
Interior of the Kidney :
- Just inside the hilum, the ureter is dilated called as pelvis of ureter.
- This is divided into 2 to 3 major clayx’s. Each major calyx is divided into 2 to 3 minor calyxs.
- The remaining part of kidney is divided into outer cortex and inner medulla.The medulla is composed of renal pyramids.
- The cortex is composed of cortical arches.
- Part of the cortex will extend between the pyramids. This is called as renal columns.
Applied Anatomy :
·
Inflamation of kidneys : Nephritis.
·
Failure of the function of kidney :
Renal failure.
· ( The most common cause for renal failure
is diabetes and hypertension. )
